Oracle E-Business Suite is one of the most comprehensive suite of integrated, global business applications used by many organization around the globe. Clients usually host E-Business Suite environment In-house which requires upfront investment and ongoing maintenance costs. This approach is proven to be non-scalable and non-flexible for the rapidly changing business needs. Cloud solutions are the way to go for these applications. Oracle Cloud Solutions with all their features and integrated security can handle the robust and complex architectures of the E-Business suite seamlessly. Oracle EBS on cloud can help organizations with its scalability, elasticity and performance at much lower costs.
Please note that the cloud world is changing very fast and technology components/configurations which are valid today may get modified or completely replaced by something better. It is important to keep track of the latest technology evolution. A reference section has been added to end of this article which points to dynamic documents/information maintained by Oracle related to the information discussed in this article.
Last part of this article also points out how the current and planned future changes in technology world, fueled by Cloud computing and automation, will impact the Oracle Apps DBA /Oracle DBA job responsibilities.
Before we go further it is important to understand the difference between SaaS/PaaS/IaaS offerings on which Oracle Cloud Strategy is based on:
1. SaaS (Software as a service)
SaaS uses the web to deliver applications that are managed by Oracle and whose interface is accessed on the clients’ side. Most SaaS applications can be run directly from a web browser without any downloads or installations required but some SaaS applications require plugins.
So in this strategy Oracle will manage everything which is needed to run the application: applications software, runtime, data, middleware, OSes, virtualization, servers, storage and networking.
Besides Oracle, other major SaaS examples in market: Salesforce, Workday, Concur, Cisco WebEx etc
2. PaaS (Platform as a service)
With PaaS technology, enterprise operations, or a third-party provider, can manage OSes, virtualization, servers, storage, networking, and the PaaS software itself. Developers, however, manage the applications.
Applications using PaaS inherit cloud characteristic such as scalability, high-availability, multi-tenancy.
Oracle DBaaS is one such an example of PaaS
3. IaaS (Infrastructure as a service)
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), are self-service models for accessing, monitoring, and managing remote datacenter infrastructures, such as compute (virtualized or bare metal), storage, networking, and networking services (e.g. firewalls).
This gives an excellent option to clients to not purchase hardware and instead can purchase IaaS resources based on consumption, similar to electricity or other utility billing.
IaaS users are responsible for managing applications, data, runtime, middleware, and OSes.
IaaS Providers like Oracle still manage virtualization, servers, hard drives, storage, and networking.
Advantage here is that user can install any required platform on top of IaaS.
IaaS is like running a ‘virtual’ computer/server on cloud (remote data center).
You will get elastic storage/compute/Network resources which you can scale in/out on will with minimal efforts.

Image Source: Oracle Site.
Oracle EBS Offering on Oracle Cloud
Key offerings for running Oracle EBS on Oracle Cloud are:
Single Node EBS Installation on Oracle Cloud
The single node on IaaS option consists of an all-in-one Oracle E-Business Suite Release 12.2.5 machine image that includes both the application tier and the database tier. Available on Oracle Cloud Marketplace, this image is updated when required, so you can quickly provision the latest image to explore new features. Oracle Market place (discussed later in this article) gives option of install EBS as fresh install or with demo database.
This option is ideal if you wish to evaluate and test standard Oracle E-Business Suite functionality, and become familiar with the technology components and other features.
Multi Node EBS installation on Oracle Cloud
For multi-node EBS installation Oracle has provided multiple provisioning options as database tier can be run on Compute Nodes or DBCS or ExaCS (for extreme performance requirements). Application Tier will always run on Oracle Compute nodes.
So here you can have many options to get EBS installed as per requirements.
For both demo and fresh install purpose:
- On the application tier you can have single node, multi-node shared, multi-node distributed
- On the database tier you can have single node database on Compute/DBCS/ExaCS or multiple node database on DBCS/ExaCS.
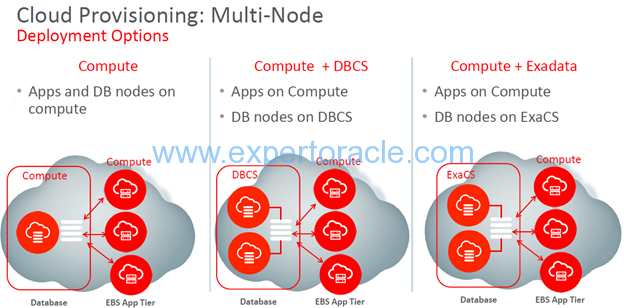
Image Source: Oracle Site.
Running database on DBCS/ExaCS gives users access to many automated tools developed by Oracle to orchestrate and manage database resources efficiently.
Lift ‘n’ Shift Approach
Oracle approach to migrate E-Business instances from on-premise to Cloud is named “Lift ‘n’ Shift”. This is an efficient and automated cloning method. Oracle has created a clone utility which makes it easy for users to backup the on-premise EBS setup and restore it on the Oracle Cloud servers.
The cloud copy can be used for testing or development, and—when when you are ready—as part of a permanent migration of your production environment to the cloud.
The Lift and Shift process is supported for:
» Oracle E-Business Suite Release 12.2.3 and higher
» Oracle E-Business Suite Release 12.1.3
Please go through Doc ID 2066260.1 to understand more on this approach and Oracle Cloud offerings related to Oracle EBS.
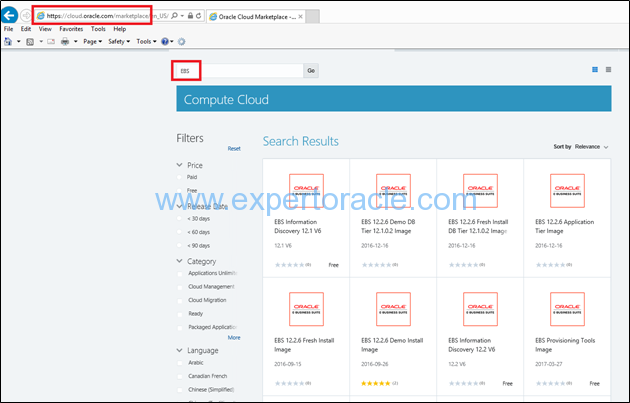
Oracle Cloud Marketplace
Oracle Cloud Marketplace helps Oracle Cloud customers find the best applications to meet their needs through an easily searchable interface.
Besides Oracle Cloud customers, the Oracle Cloud Marketplace brings a new cloud applications distribution channel to Oracle partners, enabling them to reach Oracle’s customer base
You will find many E-Business Suite Images on Oracle Cloud Marketplace which can be used directly to install EBS applications with significantly less efforts.
Upcoming advancements in running Oracle EBS on Oracle Cloud
Oracle is very bullish on Cloud computing and putting huge efforts in making Oracle Cloud more user friendly by adding new features constantly. Some of the automation roadmap activities that Oracle has planned are:
- Fast Cloning – Creating and automating Compute snapshots to reduce timing as well as complexity of the EBS cloning process.
- Automated Scaling – For the addition/removal of Nodes/CPU/Memory
- Automated Backup & restore – Efficient EBS and database backup/restore with minimal human effort.
- Disaster recovery process streamlining and automated failover – On-Premise to cloud, Cloud to Cloud, Automated failover
- Improved Integration between Cloud Applications
Benefits of running Oracle EBS on Oracle Cloud
- Lower Cost of Application Ownership
Customer do not pay upfront capital expenditures. All payments are subscription based, pay for use kind of. On top of it, Oracle Cloud promises Standardization, Predictable and consistent performance for their applications.
- Increase Business Agility
Any kind of computing/storage/network resource can be added based on immediate/planned business or process changes.
- Optimum Resource utilization
Reduced administration overhead. Several automated Oracle tools on Cloud help in cutting down IT personnel workload.
- Reduced Risk
Enterprise grade secured global infrastructure to meet Industry compliance requirements. Built in Oracle data center disaster recovery can be leveraged very easily
- Visibility & Transparency
Having all technology components getting sourced from single location give top management complete visibility of what resources are getting consumed, for what purpose and how efficiently.
Changing role of the database administrator in the “Cloud Era.”
Demand for traditional DBA role is not just affected by emerging of cloud computing. It has also been affected by more and more self-managing and automated RDBMS databases (and applications).
Example 1:
EARLIER:
Installing fresh EBS instances for demo/testing required proper planning, server procurement, OS setup, Pre-requisite fulfillment for database/application, network resource allocations etc etc. It used to take DBA a long time to coordinate with multiple teams and put significant effort to get it installed.
NOW:
As explained above, installing EBS instance is now as simple job as clicking some series of mouse buttons. No hard-core DBA skills required.
EXAMPLE 2:
EARLIER:
Installing RAC setup required deep understanding of network, storage and cluster/database software. Getting an experienced DBA to install multi-Node RAC system itself was a big challenge for some organizations.
NOW:
Oracle has automated the RAC install steps. You just need to mention on the Cloud console that you need clustered database and Oracle automated processes will get it created.
There are many more such changes which are already available or about to be launched like automated backup/recovery process, automated cloning, automated failover processes, automated patching etc. This essentially means that traditional DBA’s scope of work (as well as dependency on DBA) will get reduced further.
It also seems evident that Cloud migrations coupled with Automation will impact those IT jobs most which are focused on configuring and maintaining infrastructure. Companies simply won’t need as much DBAs or Sysadmins. Who needs a DBA to install and configure a new Oracle RAC database when you can do it in a few mouse clicks? Who needs a DBA to create a backup and recovery plan when cloud services are offering them out of the box? Yes, a SME will be needed to take architectural decisions but much of actual hand-on DBA work will be automated.
Traditional Oracle DBA/Oracle Apps DBAs need to upskill/cross skill to remain relevant in this constantly changing technology world. It can be an entirely new skill like learning Non-relational databases like NOSQL, learning Multi-tenancy and data partitioning concepts on Cloud, new tools and concepts behind monitoring a Cloud Database, learning concepts of container applications like Docker, Data analytics skills, Big Data/Hadoop skills etc.
Gartner analysts have mentioned in 2009 that “Any large-scale shift to cloud computing is a decade or more away”. ‘Cloud’ was a buzzword at that time but mass migration to Cloud and complete shutdown of on premise data center was not very common.
Fast forward to 2017 and now we are indeed seeing that many small and big organizations are lining up to purchase cloud computing resources and planning to shut down their data center completely.
Reference:
Getting Started with Oracle E-Business Suite on Oracle Cloud (Doc ID 2066260.1)
Oracle EBS and Oracle Cloud Blog : https://blogs.oracle.com/EBSandOracleCloud/
Oracle white paper: http://www.oracle.com/us/products/applications/ebs-on-oracle-cloud-3220296.pdf
Oracle EBS on Oracle Cloud FAQ: http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E72030_01/infoportal/ebscfaq.html
Oracle Cloud Marketplace: https://cloud.oracle.com/marketplace/product/compute?_afrLoop=3745783946586083&_afrWindowMode=0&_afrWindowId=null
Please share your thoughts/opinions in comment section.
- Oracle Multitenant DB 4 : Parameters/SGA/PGA management in CDB-PDB - July 18, 2021
- Oracle Multitenant DB 3 : Data Dictionary Architecture in CDB-PDB - March 20, 2021
- Oracle Multitenant DB 2 : Benefits of the Multitenant Architecture - March 19, 2021


Thanks Brijesh you have nicely covered both Database and Application whcih are important for any Apps DBA.